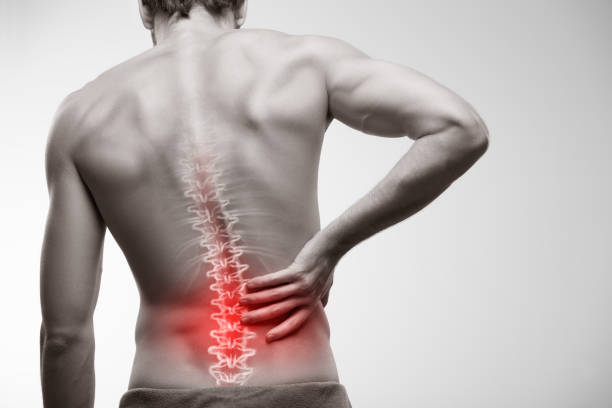
Lower back soreness is a common complaint affecting people of all ages. While most cases are mild and temporary, some can indicate serious underlying conditions that require medical attention. Understanding the causes, risk factors, and warning signs can help you determine when it’s time to seek emergency care.
What is Lower Back Soreness?
Lower back soreness refers to discomfort, stiffness, or pain in the lumbar region of the spine. This pain can range from mild to severe and may be temporary or chronic. The lower back supports much of the body’s weight and movement, making it prone to strain, injury, and wear and tear.
Common Symptoms of Lower Back Soreness
- Dull or sharp pain in the lower back
- Stiffness and reduced range of motion
- Pain that worsens with movement or prolonged sitting
- Muscle spasms or tightness
- Numbness or tingling in the legs
What Are the Causes of Lower Back Pain?
Lower back pain can have multiple causes, ranging from muscle strain to serious medical conditions. The most common reasons include:
Muscle Strains and Sprains
Muscle strains and sprains are among the most common causes of lower back pain. They occur due to improper lifting techniques, sudden movements, or twisting motions that strain the muscles and ligaments. Poor posture and prolonged sitting can also contribute to back strain, as can excessive physical activity without proper stretching or warm-ups.
Herniated or Bulging Discs
Herniated or bulging discs occur when the discs between the vertebrae protrude and press on nearby nerves. This can result in sharp pain, numbness, or tingling sensations in the lower back and legs. Herniated discs often develop due to aging, repetitive stress, or heavy lifting.
Degenerative Disc Disease
Degenerative disc disease is an age-related condition in which the spinal discs wear down over time. This leads to chronic lower back pain and stiffness, making daily activities more challenging. As the discs lose their cushioning ability, movement can become more painful and restricted.
Sciatica
Sciatica occurs when the sciatic nerve is compressed, leading to pain that radiates down the leg. This condition is often caused by a herniated disc, spinal stenosis, or injury to the lower back. Sciatica can result in a sharp, shooting pain that makes standing or walking difficult.
Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis is a condition characterized by the narrowing of the spinal canal, which places pressure on the nerves. It is most common in older adults and can cause lower back pain, numbness, and weakness in the legs. Symptoms may worsen with prolonged standing or walking.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative condition that affects the cartilage in the spine. As the cartilage wears down, the bones rub against each other, causing pain and stiffness. Osteoarthritis is most common in older adults and can lead to limited mobility and chronic discomfort.
Kidney Stones or Infections
Severe lower back pain can sometimes be a sign of kidney stones or infections. Kidney-related pain is often accompanied by additional symptoms such as fever, nausea, and painful urination. If left untreated, kidney infections can lead to serious complications.
Infections and Tumors
Although rare, infections and tumors can cause persistent lower back pain. Spinal infections may develop due to bacteria or viruses, leading to inflammation and discomfort. Cancerous tumors affecting the spine can also result in severe, unrelenting pain that does not improve with rest or medication.
Pregnancy-Related Back Pain
Pregnancy places additional strain on the lower back due to weight gain and hormonal changes. As the body adjusts to accommodate the growing baby, many women experience lower back soreness. Proper posture, gentle exercises, and prenatal support belts can help alleviate discomfort during pregnancy.
Is It Better to Sit or Lay Down with Lower Back Pain?
Finding the right position for lower back pain relief depends on the cause and severity of discomfort. Here are some guidelines:
- Sitting: Use a chair with lumbar support and keep feet flat on the ground. Avoid slouching.
- Lying Down: Sleeping on your side with a pillow between your knees can help maintain spinal alignment.
- Standing and Walking: Staying active can prevent stiffness and promote healing.
- Stretching and Strengthening Exercises: Gentle movements can improve flexibility and reduce pain.
Who is at a Higher Risk of Facing a Back Pain Emergency?
Certain individuals are more prone to severe back pain that requires medical intervention. Risk factors include:
- Older Adults: Age-related degeneration increases the risk of serious conditions.
- Athletes and Manual Laborers: High-impact activities and repetitive movements can strain the back.
- People with Obesity: Excess weight puts additional stress on the spine.
- Individuals with Preexisting Conditions: Osteoporosis, arthritis, or a history of back problems increase the likelihood of complications.
- Pregnant Women: Hormonal changes and weight gain contribute to lower back pain.
- People with a Sedentary Lifestyle: Weak muscles and poor posture can lead to chronic pain.
How Do You Know If Your Lower Back Pain is Serious?
While most cases of lower back pain are not life-threatening, certain symptoms indicate a more serious condition. If you experience severe or worsening pain that does not improve with rest, it may be a sign of a deeper issue. Pain that radiates down one or both legs, especially below the knee, could indicate nerve compression. Additionally, numbness, tingling, or weakness in the legs or feet may signal nerve damage. If your pain follows a fall, accident, or injury, or if you have difficulty walking or standing due to extreme weakness or instability, seeking medical evaluation is crucial.
When is Back Pain Serious Enough to go to the ER?
You should visit the emergency room if you experience:
- Sudden, intense pain that is unbearable
- Severe pain after a traumatic injury (e.g., car accident, fall)
- Numbness, weakness, or paralysis in the legs
- Difficulty controlling bladder or bowel functions
- Fever with persistent back pain
- Sharp, shooting pain accompanied by abdominal discomfort
- A history of cancer with new, unexplained back pain
Ignoring these symptoms can lead to permanent nerve damage or serious complications.
How Emergency Rooms Treat Lower Back Pain
If you visit the ER for severe lower back pain, doctors will assess your condition using:
1. Medical Evaluation
Discussing symptoms, medical history, and possible triggers
2. Physical Examination
Checking for signs of nerve compression, muscle weakness, or spinal instability
3. Diagnostic Imaging
4. X-rays: Detect fractures or spinal misalignment
5. CT Scans and MRIs: Identify herniated discs, infections, or tumors
6. Blood Tests: Check for infections or inflammatory conditions
7. Pain Management
8. Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, or corticosteroid injections
9. IV Fluids: If dehydration or infection is present
10. Emergency Interventions
- Surgical Consultation: If nerve damage, fractures, or serious conditions are detected
- Spinal Injections: To reduce inflammation and provide pain relief
- Referral to Specialists: For long-term treatment plans
Life Savers ER: Get Expert Care When You Need It
Persistent or severe back pain should never be ignored. At Life Savers ER, we offer comprehensive emergency care, including X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and advanced pain management treatments to diagnose and relieve back pain effectively. With three Houston ER locations and no wait times, our experienced medical team is available 24/7 to provide the care you need when you need it.
Don’t suffer through the pain—visit Life Savers ER for immediate, expert back pain treatment today!
Life Savers 24 Hour Emergency Room is equipped to handle life threatening conditions quickly. Your emergency or concern is our priority! Life Savers 24 Hour Emergency Room is your Houston ER for immediate definite care. Do not hesitate to call us today or stop by one of our houston emergency room locations: Willowbrook ER, Heights ER, or Summerwood ER.





